New to KubeVault? Please start here.
Monitoring Vault Server Using CoreOS Prometheus Operator
The prometheus server is needed to configure so that it can discover endpoints of services. If a Prometheus server is already running in cluster and if it is configured in a way that it can discover service endpoints, no extra configuration will be needed.
If there is no existing Prometheus server running, read this tutorial to see how to install CoreOS Prometheus Operator.
This tutorial will show you how to monitor Vault server using Prometheus via CoreOS Prometheus Operator.
Monitor Vault server
apiVersion: kubevault.com/v1alpha1
kind: VaultServer
metadata:
name: exampleco
namespace: demo
spec:
nodes: 1
version: "0.11.1"
serviceTemplate:
spec:
type: NodePort
backend:
inmem: {}
unsealer:
secretShares: 4
secretThreshold: 2
mode:
kubernetesSecret:
secretName: vault-keys
monitor:
agent: prometheus.io/coreos-operator
prometheus:
namespace: demo
labels:
app: vault
interval: 10s
Here,
monitor.agentindicates the monitoring agent. Currently only valid value currently iscoreos-prometheus-operatormonitor.prometheusspecifies the information for monitoring by prometheusprometheus.namespacespecifies the namespace where ServiceMonitor is created.prometheus.labelsspecifies the labels applied to ServiceMonitor.prometheus.portindicates the port for PostgreSQL exporter endpoint (default is56790)prometheus.intervalindicates the scraping interval (eg, ’10s’)
Now create Vault server with monitoring spec
$ kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubevault/docs/master/docs/examples/monitoring/vault-server/vault-server-coreos.yaml
Vault operator will create a ServiceMonitor object once the Vault server is successfully running.
$ kubectl get servicemonitor -n demo
NAME AGE
vault-demo-exampleco 23s
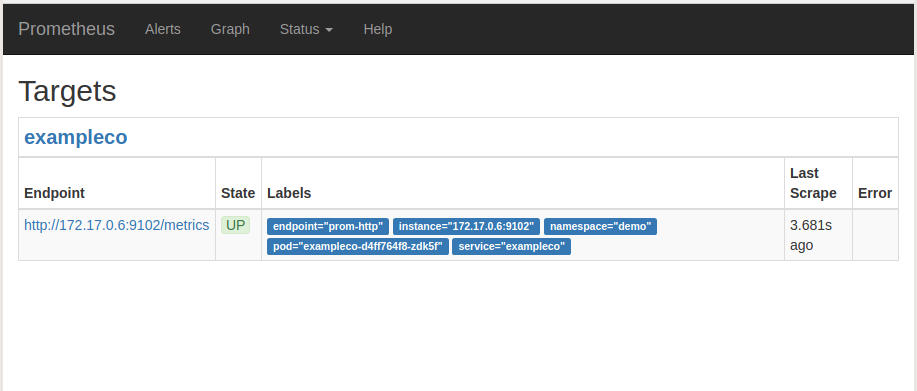
Now, if you go the Prometheus Dashboard, you should see that this database endpoint as one of the targets.
Cleaning up
To cleanup the Kubernetes resources created by this tutorial, run:
$ kubectl delete -n demo vs/coreos-prom-postgres
$ kubectl delete ns demo